Hiring the wrong drone operator costs more than money. Inaccurate survey data leads to flawed design decisions. Lapsed insurance leaves you exposed if something goes wrong on-site. Unregistered pilots put your project at legal risk before it even starts. The difference between a professional commercial drone operator and someone who bought a drone last month is not always obvious from a website or a quote.
This guide gives you 15 specific questions to ask before you commit. Whether you are commissioning a building inspection, a topographical survey, or aerial photography for a development project, these questions separate competent, insured professionals from operators cutting corners.
Drone Services Ireland has operated commercially since 2016 and is a founding member of Drone Professionals Ireland. We wrote this guide because we believe informed buyers make better decisions, and better decisions raise standards across the entire Irish drone industry.
Last Updated: February 2026
Table of Contents
Regulatory Compliance and Licensing
Q1. Are You Registered as a UAS Operator with the IAA?
Every commercial drone operator in Ireland must hold a valid IAA registration through the MySRS platform. Registration costs €40 for two years and generates a unique Operator ID that must be displayed on every aircraft and uploaded to the drone’s Remote ID system. Registration is mandatory for any drone over 250 grams or any drone equipped with a camera capable of capturing personal data.
Ask for the operator’s IAA registration number and verify it is current. Unregistered operators face enforcement action, fines, and automatic invalidation of insurance. If someone cannot produce a registration number on request, that tells you everything you need to know about their professional standards.
Q2. What Pilot Competency Certificates Do Your Pilots Hold?
Irish drone pilots must hold certificates appropriate to their operational category. The A1/A3 certificate is the basic qualification, obtained through online training and a 40-question examination. The A2 certificate is the advanced qualification that permits operations closer to uninvolved people and requires a practical examination at an IAA-recognised testing centre. Both certificates are valid for five years.
Operations that go beyond Open Category limits, such as flights beyond visual line of sight (BVLOS), above 120 metres, or inside controlled airspace, require Specific Category operational authorisation. This involves a formal risk assessment using the SORA (Specific Operations Risk Assessment) methodology, a detailed operations manual, and training at an IAA-approved facility. Processing times for Specific Category authorisations can run to 16 weeks or longer.
Ask to see the physical certificate. Verify the pilot’s qualification level matches what your project actually requires. An operator holding only A1/A3 certification cannot legally conduct work that demands A2 or Specific Category permissions, regardless of how experienced they claim to be.

Q3. Do You Comply with Current EASA Regulations?
Ireland operates under the harmonised EU regulatory framework established by EASA through Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2019/947. The IAA is Ireland’s national competent authority for implementing and enforcing these EU-wide standards.
Professional operators should demonstrate familiarity with the regulations that came into effect on 1 January 2024, including mandatory class identification labels on new drones, strict Remote ID requirements, and UAS geographical zones that restrict flying near airports, prisons, hospitals, and critical infrastructure. You can check Irish airspace restrictions on our drone airspace map.
Ask how the operator stays current with regulatory changes. Membership in professional bodies such as Drone Professionals Ireland demonstrates a commitment to ongoing professional development.
Insurance and Professional Protection
Q4. What Insurance Coverage Do You Carry?
Third-party liability insurance is legally mandatory for all commercial drone operations in Ireland. The minimum coverage is €1 million, though professional operators typically carry between €5 million and €13 million for high-value commercial projects. This insurance covers compensatory damages for accidental bodily injury and third-party property damage, in line with EU Regulation 785/2004.
Request a current certificate of insurance and check three things: the coverage amount, the policy dates, and whether it explicitly covers commercial drone operations. Standard home insurance policies exclude drone activities entirely, making aviation-specific cover essential.
Beyond mandatory liability cover, professional operators should carry professional indemnity insurance. This protects you against claims arising from negligent advice or inaccurate deliverables, which matters particularly for surveying and mapping projects where accuracy directly affects design decisions.
Q5. How Do You Handle GDPR and Data Protection?
The General Data Protection Regulation applies to all drone operations that capture personal data, which includes footage showing identifiable faces, addresses, vehicle registrations, or behavioural patterns. The Irish Data Protection Commission published specific drone guidance outlining transparency requirements, lawful basis for processing, and data subject rights.
Professional operators must establish a lawful basis for data collection, typically through legitimate interest assessments. They should implement transparency measures including visible identification on site, privacy notices, and a published privacy policy explaining data collection purposes, retention periods, and data subject rights.
Ask about data retention. Professional operators typically retain personal data for 30 to 90 days unless contractual, legal, or insurance purposes require longer. Verify that storage is encrypted and that the operator can respond to data subject access requests within the required 30-day timeframe.
Equipment, Accuracy, and Technical Capabilities
Q6. What Equipment and Sensors Do You Use?
Professional surveying requires capabilities far beyond a consumer drone. Survey-grade photogrammetry demands cameras with at least 20-megapixel resolution, ideally with a full-frame sensor reaching 42 to 61 megapixels. A global shutter outperforms a rolling shutter for accurate geometric capture, and three-axis gimbal stabilisation is essential for consistent image quality.
The single biggest differentiator is positioning technology. RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) or PPK (Post-Processed Kinematic) GNSS systems deliver 1 to 5 centimetre accuracy, compared with standard GPS accuracy of 1 to 3 metres. In practical terms, RTK provides corrections in flight via a base station, while PPK applies corrections during post-processing. Both achieve survey-grade results; PPK is more reliable in areas with poor radio signal.
Ask for specific equipment model numbers and technical specifications. Also, ask about ground control points (GCPs). These are surveyed reference markers placed on the ground before the flight. Professional operators typically deploy 1 GCP per 25 to 50 acres, surveyed to sub-centimetre accuracy with RTK GPS or a total station.

Q7. What Accuracy Can You Guarantee, and How Do You Verify It?
Professional surveying follows ASPRS (American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing) standards, which measure accuracy using Root Mean Square Error (RMSE). In plain terms, RMSE tells you how far, on average, the survey data points are from their true positions on the ground. Professional operators should achieve horizontal accuracy of 1.5 to 5 centimetres and vertical accuracy of 2 to 5 centimetres with proper RTK/PPK implementation.
Ask about Ground Sample Distance (GSD). This is the real-world size of each pixel in the aerial image. Professional work typically achieves a GSD of 1 to 3 centimetres, with accuracy approximately three times the GSD under optimal conditions.
For topographical surveys in Ireland, verify the operator is familiar with SCSI (Society of Chartered Surveyors Ireland) accuracy bands. Engineering surveys typically demand Band C accuracy (plus or minus 5 to 10 mm plan), while general topographic work may accept Band E or F (plus or minus 25 to 50 mm). If the operator does not know what SCSI accuracy bands are, that tells you something.
Q8. Do You Offer Thermal Imaging for Building Inspections?
Survey-grade thermal imaging requires specific sensor capabilities. Look for a minimum resolution of 640 by 512 pixels with thermal sensitivity below 0.05 degrees Celsius. The temperature range should span minus 20 to plus 150 degrees Celsius, with accuracy of plus or minus 2 degrees Celsius or 2 per cent of the reading.
Professional roof inspections follow ASTM Standard C1153, which specifies that inspections must occur after sundown to avoid solar thermal loading, with a minimum 10-degree temperature differential between the underside of the deck and the roof surface. Surfaces must be free of standing water, snow, ice, or debris. Each thermal camera requires calibration certification.
Ask whether the operator captures both RGB and thermal imagery simultaneously. Dual-capture allows direct comparison, with georeferenced anomaly locations plotted on both visual and thermal maps. Deliverables should include thermal orthomosaics, visual orthomosaics for context, detailed anomaly reports with GPS coordinates and temperature readings, and prioritised repair recommendations.
Q9. Do You Have LiDAR Survey Capability?
LiDAR surveying uses laser pulses to measure distances and build highly accurate 3D models of terrain and structures. Its key advantage over photogrammetry is vegetation penetration: LiDAR can see through the tree canopy to map the ground beneath, which photogrammetry cannot do. It also works in low light and captures vertical structures like power lines and building facades with greater precision.
Survey-grade LiDAR sensors achieve 1 to 2 centimetre accuracy with measurement rates exceeding 240,000 points per second in single-return mode. Professional systems capture multiple returns per pulse, typically 3 to 5 returns, enabling bare-earth detection beneath dense canopy.
Verify the operator uses high-precision GNSS with RTK or PPK and an inertial measurement unit (IMU) for trajectory determination. Ask about point cloud classification capabilities. Professional processing separates ground, vegetation, buildings, and other features, enabling the extraction of a bare-earth Digital Terrain Model for flood modelling, utility corridor surveys, and infrastructure planning.
H2: Deliverables, Formats, and Quality Control
Q10. What Deliverables Will I Receive, and in What Formats?
Standard surveying and mapping deliverables should include orthomosaic maps in georeferenced GeoTIFF format, 3D point clouds in LAS or LAZ format, Digital Surface Models (DSM) and Digital Terrain Models (DTM), contour maps, and CAD extractions in DWG or DXF format. All deliverables must be georeferenced to a specified coordinate system with metadata documenting capture date, accuracy, and coordinate reference.
For Irish projects, verify that the operator uses Irish Transverse Mercator (ITM) as the coordinate reference system, which is the most accurate national system. Height datum should reference Malin Head (OGM15), updated from OSGM02 in August 2016. Legacy Irish Grid conversions may introduce positional errors.
For aerial photography, request RAW format capture in DNG alongside processed JPEG or TIFF files. Video should meet a minimum of 4K resolution at 30 frames per second, with professional projects increasingly requiring 5K to 8K capture for large commercial properties.

Q11. What Quality Control Processes Do You Follow?
Professional operators implement quality control beyond simply completing the flight. For photogrammetry projects, this means verifying that RMSE values meet the accuracy thresholds agreed before the project started. Independent checkpoint analysis validates accuracy using control points that were not incorporated into the processing algorithms, providing an unbiased measure of true accuracy.
Ask about Safety Management Systems. Professional operators following ISO 21384-3 demonstrate a commitment to operational excellence through documented safety policies, risk management frameworks, safety monitoring, and a safety-promotion culture. This international standard provides a framework covering quality, safety, security, and operational protocols.
For thermal inspections, deliverables should document weather conditions, equipment calibration verification, thermal scaling, and the methodology standard followed (typically ASTM C1153 for roof inspections).
Understanding Drone Survey Costs in Ireland
Q12. How Is the Project Priced, and What Is Included?
Drone survey costs in Ireland vary depending on site size, survey type, required deliverables, and equipment needs. As a general guide, a straightforward aerial photography or video shoot for a small site might start from €400 to €600 plus VAT. A survey-grade photogrammetry survey of a site under 50 acres typically falls in the €800 to €2,000 range. LiDAR surveys, which require more expensive equipment and longer processing times, generally start at €1,500 for smaller sites.
Ask what is included in the quoted price. A professional quote should cover pre-flight planning, site attendance, data capture, processing, and delivery of specified outputs. Watch for quotes that exclude processing, ground control points, or deliverables as add-ons, as these can significantly increase the final cost.
Be cautious of quotes that seem unusually low. A drone survey is not just a flight; it is a data capture and processing exercise that requires calibrated equipment, trained personnel, proper insurance, and professional software. If someone quotes half what everyone else does, ask yourself what they are leaving out.
Professional operators can typically demonstrate that a drone survey delivers 60 to 70 per cent cost savings compared with traditional ground-based surveying, with faster turnaround and more comprehensive coverage.
Red Flags When Hiring a Drone Operator
Q13. What Warning Signs Should I Watch For?
Not every operator who owns a drone is qualified to deliver commercial work. Here are the warning signs that should give you pause:
Cannot produce an IAA registration number on request. This is the absolute minimum legal requirement. If they hesitate or claim they do not need one, walk away.
No aviation-specific insurance. Standard business insurance and home insurance do not cover commercial drone operations. Ask to see the certificate. If they say they are “covered” but cannot produce documentation, they are not covered.
Uses consumer-grade equipment for survey work. A DJI Mini or Mavic Air is a capable recreational drone, but it lacks RTK positioning, sufficient sensor resolution, and the payload capacity required for survey-grade work. Ask what platform they fly.
Cannot explain their accuracy methodology. If the operator cannot tell you what RMSE they achieve, what GSD they target, or how they verify accuracy using independent checkpoints, they are not delivering survey-grade data.
No portfolio or case studies. Professional operators should be able to show you examples of completed projects similar to yours. Ask for references you can contact.
Quotes without seeing the site or understanding the brief. A professional will ask detailed questions about your site, deliverables, accuracy requirements, and timeline before providing a quote. Anyone who quotes a flat rate without understanding what you need is guessing.
Claims to do everything. Survey, photography, videography, wedding shoots, estate agent work, and industrial inspection all require different equipment, skills, and experience. Be wary of operators who claim expertise across every category.
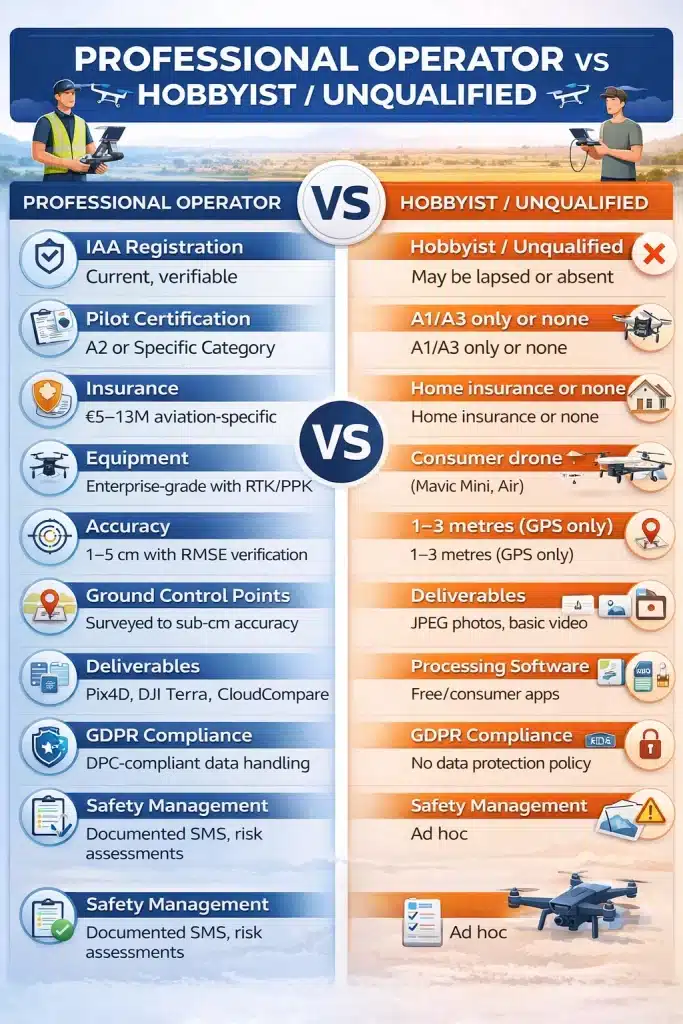
Professional Operator vs Hobbyist: Quick Comparison
What to Expect After You Hire a Drone Operator
Q14. What Does the Process Look Like from Booking to Delivery?
If you have never commissioned drone services before, here is what a typical project looks like with a professional operator:
Step 1: Brief and scoping. You describe the site, the purpose of the survey or inspection, the deliverables you need, and any deadlines. The operator reviews the site boundary (usually from a KML file or map screenshot), checks airspace restrictions, and confirms whether the work falls under Open or Specific Category operations.
Step 2: Quote and agreement. The operator provides a detailed quote specifying what is included: planning, site attendance, data capture, processing, deliverable formats, accuracy targets, and timeline. You receive a formal agreement covering scope, data ownership, GDPR obligations, and insurance details.
Step 3: Pre-flight planning. The operator plans flight paths, determines GCP placement, checks weather forecasts, and completes a site-specific risk assessment. For Specific Category work, this may involve filing with the IAA.
Step 4: Site attendance and data capture. The operator arrives, sets up GCPs (if required), conducts pre-flight equipment checks, and flies the mission. Site attendance typically takes 2 to 4 hours for a standard survey, though large sites may require a full day or more.
Step 5: Processing and quality control. Data is processed using professional software. Accuracy is verified against independent checkpoints. This stage typically takes 1 to 5 working days, depending on project complexity and the deliverables required.
Step 6: Delivery. You receive processed deliverables via secure file transfer, typically within 2 working days for standard projects. The operator should be available to answer questions about the data and provide additional exports if needed.
For real examples of this process in action, see our power line survey case study and our 300-acre solar farm project.
Q15. What Happens If Weather Delays the Project?
Irish weather is unpredictable, and professional operators build contingency into their scheduling. Most professional drones handle winds of up to 10 to 15 metres per second, but data quality suffers in suboptimal conditions. Thermal imaging and photogrammetry both require specific weather windows for reliable results.
Ask about weather monitoring and rescheduling policies before you book. A professional operator will give you a primary date and a backup date, communicate any weather-related delays promptly, and never fly in conditions that compromise data quality just to meet a deadline. Photogrammetry benefits from consistent, diffuse lighting (overcast is often better than bright sunshine), while thermal imaging requires specific temperature differentials.
If a project is time-critical, discuss this at the scoping stage. Experienced operators can often find suitable weather windows within tight timeframes by monitoring conditions closely and maintaining flexible scheduling.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ask for their Operator ID number and verify it through the IAA’s MySRS platform at iaa.mysrs.ie. Every registered operator receives a unique ID that must be displayed on all their aircraft.
At minimum, third-party liability insurance of €1 million is legally required for commercial operations. Professional operators typically carry €5 to €13 million. Ask to see the certificate and check it specifically covers commercial drone work.
At minimum, third-party liability insurance of €1 million is legally required for commercial operations. Professional operators typically carry €5 to €13 million. Ask to see the certificate and check it specifically covers commercial drone work.
RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) provides centimetre-accurate positioning corrections during flight via a base station. PPK (Post-Processed Kinematic) applies the same corrections afterwards during data processing. Both achieve survey-grade accuracy. PPK is more reliable in areas with poor radio signal or obstructed line of sight to the base station.
Professional drone surveys achieve 1.5 to 5 centimetre accuracy horizontally and 2 to 5 centimetres vertically, which is comparable to traditional survey methods. The advantage is speed and coverage: a drone can survey in hours what might take a ground team days or weeks.
No. Irish airspace has geographical zones that restrict or prohibit drone flights near airports, prisons, hospitals, and critical infrastructure. Professional operators check these restrictions during pre-flight planning. See our drone airspace map for current Irish restrictions.
At minimum, an A1/A3 certificate from online training. For operations closer to people, an A2 certificate requiring a practical exam. For complex operations (BVLOS, above 120 m, controlled airspace), Specific Category authorisation from the IAA, which requires SORA risk assessment and approved training.
Standard projects are typically delivered within 2 working days of the site visit. Large or complex projects with extensive deliverables may take up to 5 working days. Discuss timelines at the scoping stage if your project has tight deadlines.
Standard projects are typically delivered within 2 working days of the site visit. Large or complex projects with extensive deliverables may take up to 5 working days. Discuss timelines at the scoping stage if your project has tight deadlines.
Remote ID is a digital identification system, similar to a number plate for drones. It broadcasts the drone’s location, altitude, flight path, and operator ID in real time. People nearby can read this information using free smartphone apps. Remote ID has been mandatory in Ireland since 2024.
Ready to Hire a Professional Drone Operator?
Drone Services Ireland has delivered commercial drone services across Ireland since 2016. We are fully IAA registered, EASA compliant, and carry comprehensive aviation insurance. Our survey-grade equipment includes RTK-enabled platforms with photogrammetry, LiDAR, and thermal imaging capabilities.
We work with engineers, architects, construction firms, local authorities, and property managers on projects ranging from single-building inspections to 300-acre site surveys. Every project receives the same standard of planning, execution, and quality control.
Explore our services:
Drone Surveying and Mapping | Drone LiDAR Survey | Building and Roof Inspections
Construction Monitoring | Aerial Photography | Thermal Imaging
Contact us or call 087 205 2331 to discuss your project requirements.
Last Updated: February 2026




